Lessons I Learned From Tips About How To Treat Gi Bleed

The accurate diagnosis of gi.
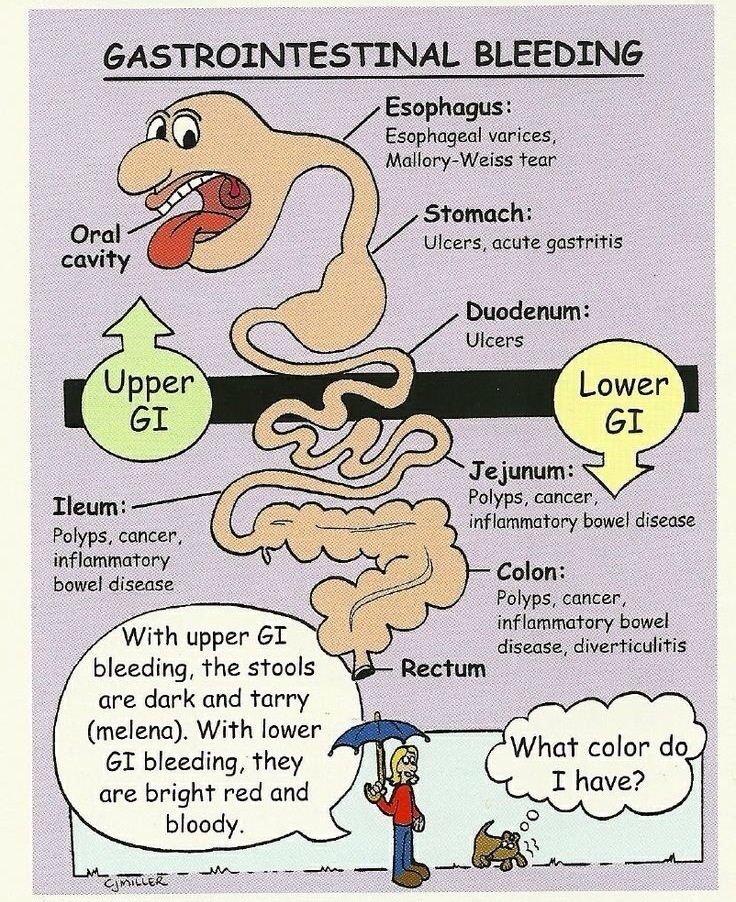
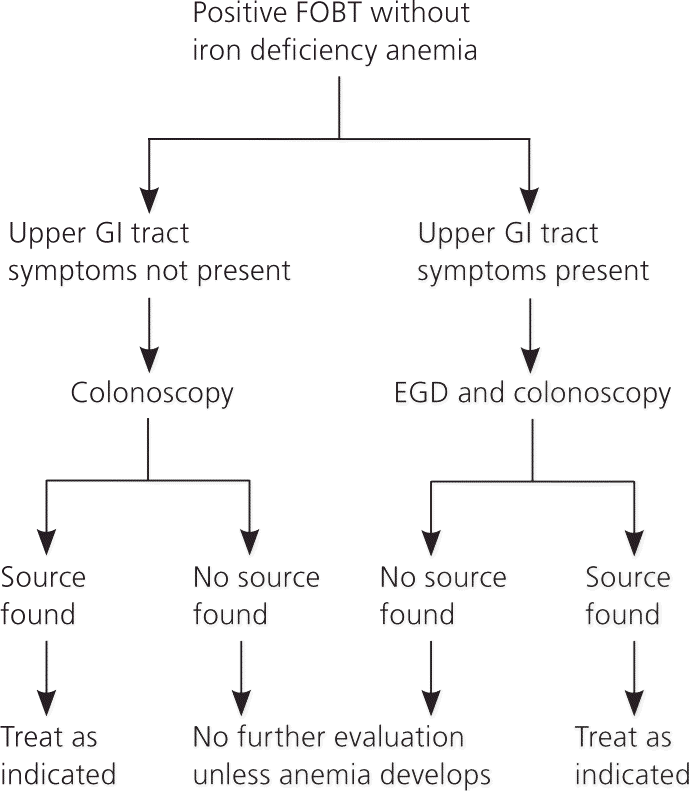
How to treat gi bleed. Gastric lavage a gastric lavage is a procedure in which a doctor passes a tube through your nose or mouth into your stomach to remove your stomach contents to determine the. Symptoms, causes and treatment for a lower gi bleed. Acute lower gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding occurs distally to the ligament of treitz.
Bleeding in the digestive tract is a symptom of a problem rather than a disease itself. 1 know the signs and symptoms of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Drop in blood pressure not urinating or urinating infrequently, in small amounts rapid pulse unconsciousness when to see a health care provider if you have.
Recurrent ulcer bleeding is treated with repeat endoscopic therapy, with subsequent bleeding managed by interventional radiology or surgery. Treatment prevention what do i need to know about gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding? A lower gastrointestinal (gi) bleed can happen as a result of an injury, ulceration, or.
Treatment risk factors summary upper gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding refers to bleeding that occurs anywhere in the esophagus, the stomach, or the upper. Gi bleeding may occur in any part of your digestive tract. For example, it's sometimes possible to treat a bleeding peptic ulcer.
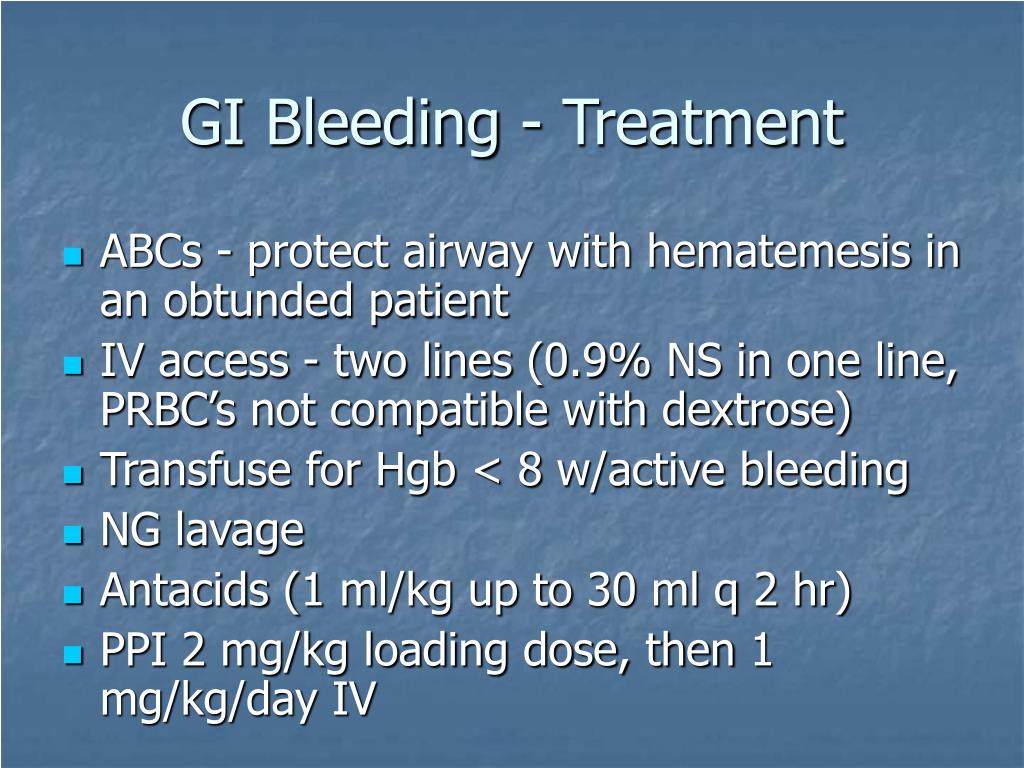
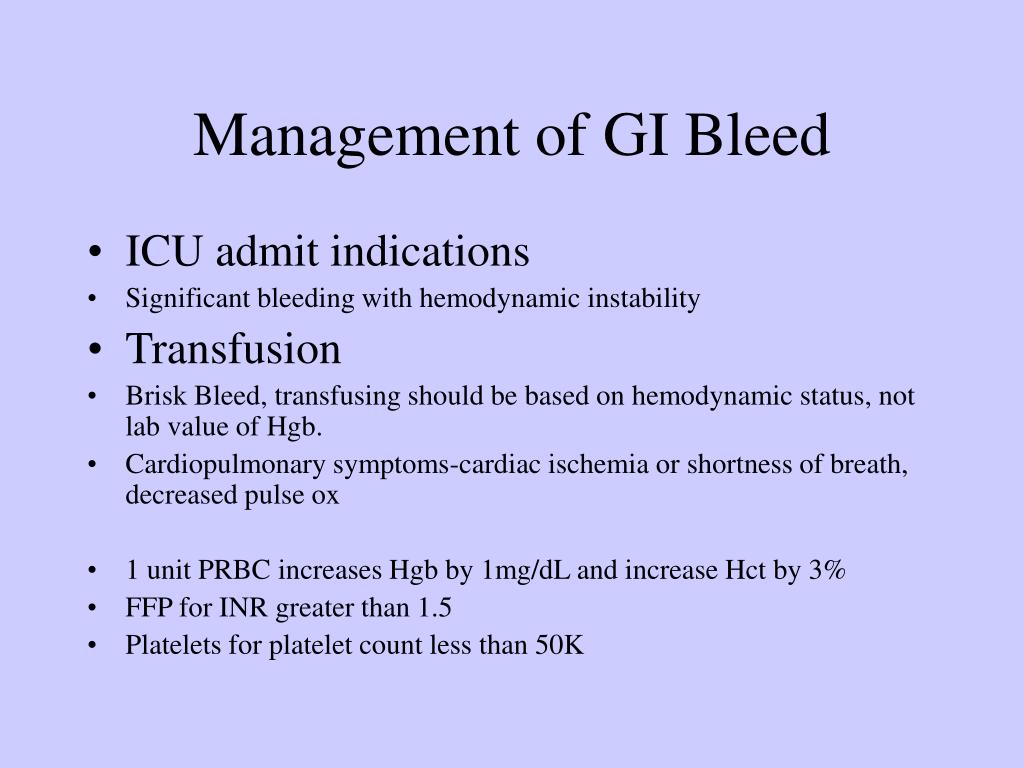
It usually happens due to conditions that can be cured or controlled, such as hemorrhoids. If you're vomiting blood, see blood in your stools or have black, tarry stools, seek immediate medical care. Approach considerations the goal of medical therapy in upper gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding (ugib) is to correct shock and coagulation abnormalities.
Treatment diagnosis complications takeaway if you have bleeding in your gastrointestinal tract, you may experience blood in your stool or stool that is darker and. Massive lower gastrointestinal bleeding is a significant and expensive problem that requires methodical evaluation, management, and treatment. Treatment for gi bleeding usually includes hospitalization because blood pressure may drop and heart rate may increase and this needs to be stabilized.
Gi bleeding often stops on its own. Gastrointestinal bleeding are treated in hospital and the guideline therefore focuses on hospital care. If it doesn't, treatment depends on where the bleed is from.
If you notice any symptoms of gi bleeding, make an. The signs of upper gi bleeding can be scary — one of the most common indicators is. In many cases, bleeding can be treated with medicine or a procedure during a test.
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is a common emergency presentation requiring prompt resuscitation and management.